It may come as something of a surprise to people struggling with mounting debt, but you have a constitutional right to file bankruptcy and get a fresh start. Article I, Section 8, of the United States Constitution empowers Congress to create “uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies.” The current bankruptcy code was enacted in 1978 and has been updated over the years.
Each state has at least one U.S. Bankruptcy Court and there is a federal court in Richmond where bankruptcy lawyers in VA can file petitions. Although the complex Bankruptcy Code and Bankruptcy Rules continue to evolve, it’s essential that everyday people understand that you have a constitutionally supported right for assistance, up to and even including discharging excessive debt should you become unable to pay.
What is Bankruptcy?
Bankruptcy is a legal solution for people struggling with debt that exceeds their income. Bankruptcy filings are often prompted by an unforeseen life change that results in financial hardship and reasonable inability to pay off a debt. For example, otherwise responsible people may be impacted by a loss of work, an illness, or a tragedy that causes a downturn in their ability to earn enough money to meet obligations.
When your debt ceiling has been breached, qualified individuals may be able to discharge the debt or create a limited repayment plan that can be successfully navigated. In essence, bankruptcy is a lawful process that helps alleviate the burden on people in debt and allows them to start a productive financial future.
Types of Bankruptcy
Although the majority of people struggling with debt generally opt for either Chapter 7 or Chapter 13, there are several types of bankruptcy filings available. These less common alternatives generally deal with niche financial issues beyond prevalent credit card debt and things like falling behind on a home loan. While somewhat rare, it’s essential that Virginians understand the full width of their options, including Chapter 7, Chapter 13, Chapter 11, and Chapter 12 are available if you qualify under federal guidelines.
Chapter 7
Chapter 7 bankruptcy is the most common type of bankruptcy and delivers relief for people overwhelmed with excessive credit card debt, medical bills, and other types of liabilities. It’s crucial to work with an experienced Virginia bankruptcy law firm.
Chapter 13: Individual Reorganization
Chapter 13 bankruptcy is a type of debt reorganization designed to allow individuals to retain assets while undergoing a restructured repayment plan. Court-approved plans generally run between three and five years and involve common consumer debts such as personal loans, mortgages, credit cards, and medical bills, among others. Although less commonly filed than Chapter 7, this debt relief process allows you to pay on house and cars and allows for unsecured debt to be discharged.
Chapter 11: Business Reorganization
This type of bankruptcy filing is generally reserved for businesses that decision-makers believe can weather a financial hardship. Chapter 11 bankruptcy calls for submitting a reorganization plan to the court within 120 days. Repayment plans are typically reviewed by creditors and may include strategies such as lowering monthly payments and discharging part of or all liabilities such as leases, contracts, and outstanding debt. The goal is generally to restore the outfit to profitability. Courts must approve or deny the Chapter 11 reorganization plan.
Chapter 12: Farming and Fishing Family Businesses
This highly specialized bankruptcy filing is referred to as “Adjustment of Debts of a Family Farmer or Fisherman with Regular Annual Income.” It is remarkably similar to the more common Chapter 13 bankruptcy filing that allows people to repay part or all of their debts over a period of time. The caveat is that this pathway will enable farmers and fishing families to continue to own and operate their business while a trustee implements a court-approved financial plan.
Reasons to File for Relief with a Virginia Bankruptcy Attorney
The decision to file for bankruptcy in Virginia should not be considered lightly. There are financial consequences to discharging debt. That being said, it’s also crucial not to remain in debt too long or exacerbate your situation. Continuing to incur debt that you cannot pay may have an even greater debilitating effect on your financial health and well-being. If you are facing any of the following financial issues, it may be time to call a Virginia bankruptcy law firm and schedule a consultation.
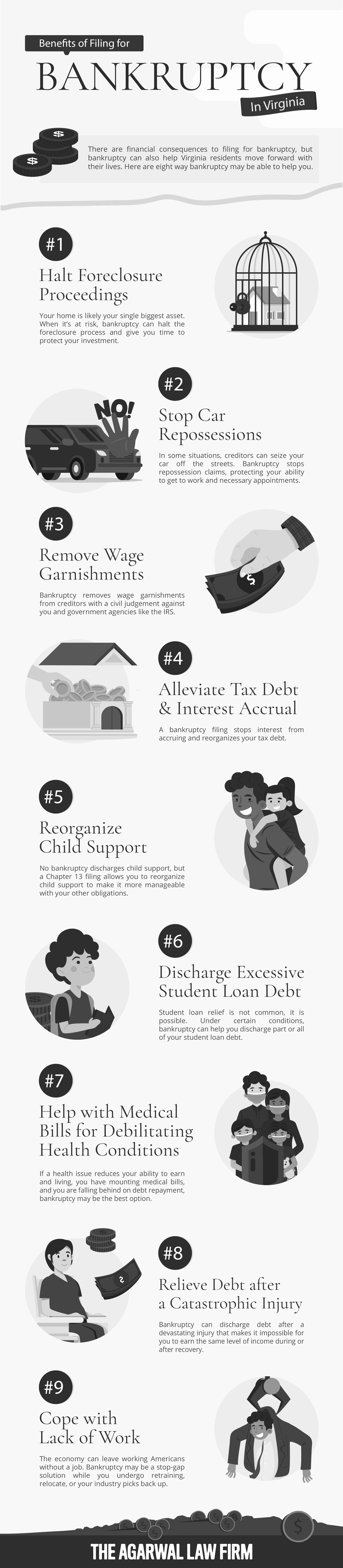
- Foreclosure Notice: If you have fallen behind on your mortgage payments, a bankruptcy filing can halt the foreclosure process and provide you time to regroup. A home is often the greatest single asset a person possesses. It’s essential to protect your investment.
- Car Repossession: When an auto loan is past due, creditors can seize it right of the streets in some cases. Filing for bankruptcy protects your ability to get to work and necessary appointments. Repossession claims are stopped during the bankruptcy process. If the car has been repossessed filing bankruptcy can help you get the car returned as long as it has not been sold.
- Wage Garnishments: When creditors gain a civil judgment against you, they can siphon money right out of your weekly paycheck. The IRS and other government agencies may not even need court approval. Diminished income only intensifies your financial struggle. A bankruptcy filing removes wage garnishments. In most cases we can retrieve the money that was garnished.
- Tax Dept: A bankruptcy filing stops interest from accruing and reorganizes your tax debt.
- Child Support: While child support is not discharged in a Chapter 7 bankruptcy filing, it can be reorganized in a Chapter 13 bankruptcy filing.
- Excessive Student Loan Debt: Success in student loan relief cases is not common, but an experienced bankruptcy lawyer can review your financial situation and make a recommendation. If you file a chapter 13 student loan creditors are forbidden from directly collecting against you while you are in your payment plan.
- Debilitating Health Conditions: If you are falling behind on debt repayment because a health issue reduces your ability to earn a living, bankruptcy may be the best option. Mounting medical bills commonly overwhelm hardworking people.
- Catastrophic Injury: It’s not uncommon for people who suffer devastating injuries to not be able to earn the same level of income during or after recovery. And tragic injuries that become chronic problems can inhibit your ability to meet previous debts. Bankruptcy can discharge debt and help restore your financial health.
- Lack of Work: The shifting economic landscape can leave working Americans without gainful employment. Bankruptcy may be a stop-gap solution while you undergo retraining, relocate, or your industry picks back up.
While each person has unique circumstances that lead them into rough financial straits, the common denominator in bankruptcy filings is that debt outweighs the revenue you are currently earning. That element is crucial to qualify for bankruptcy relief.
How Do I Qualify for Bankruptcy?
Each type of bankruptcy comes with unique qualifications. Since most people file for Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy, we’ll focus on those types for the remainder of this guide.
In order to qualify for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, individuals must first meet the standards outlined in the so-called “means test.” The test looks at your income over a six-month period and divides that figure into a monthly average. It factors in the median state income — in this case, Virginia — and accounts for localized living expenses. The basic math of the means test arrives at a conclusion of whether you have the disposable income to repay creditors while maintaining a reasonable quality of life.
In conjunction with meeting the means test standard for bankruptcy, you must wait a minimum of eight years from any previous filing before being eligible.
For those that earn above the Chapter 7 means test threshold, Chapter 13 may be a viable option. To qualify, you must not exceed unsecured and secured debt limits.
Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 13 Bankruptcy: Which Type Meets Your Needs?
The decision to file either a Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 generally requires consulting with a respected bankruptcy lawyer Virginia residents can trust. That’s because the decision to make one filing or the other comes with very specific benefits and liabilities. Neither bankruptcy filing is a one-size-fits-all solution, and an astute, seasoned bankruptcy lawyer has the knowledge to provide you with the experience and insight to make an informed decision. With that in mind, these are critical benefits to consider about Chapter 7 and Chapter 13.
Chapter 7:
- Chapter 7 eliminates unsecured debts such as credit cards, and medical bills among others.
- Chapter 7 stops harassing collections calls.
- Chapter 7 stops creditors from foreclosing on your home.
- Chapter 7 stops car repossession.
- Chapter 7 allows people to immediately start rebuilding their financial health and well-being.
Chapter 13:
- Chapter 13 allows filers to retain vital assets.
- Chapter 13 stops foreclosure and collection efforts.
- Chapter 13 may allow filers to discharge their unsecured debt by paying pennies on the dollar.
It’s important for people considering bankruptcy debt relief to understand that items such as child support, alimony, and back taxes are not generally dischargeable, but can be reorganized in a Chapter 13. When considering which pathway to take, a bankruptcy lawyer often advises filers to take a long view with regard to restoring financial security.
When Should You File for Bankruptcy in Virginia?
If you are contemplating bankruptcy, the chances are that you are nearing the point of no return financially. Some of the indicators that should prompt you to schedule a consultation with a Virginia bankruptcy attorney include civil judgments against you, inability to meet monthly bills, excessive credit card debt, receiving a foreclosure notice, or pulling money out of retirement accounts to stay afloat. If you are struggling with these or other financial hardships, it may be time to file for bankruptcy in Virginia.
How Do I File for Bankruptcy in Virginia?
It may seem almost counterintuitive, but once you file for Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy, you will likely experience a sense of relief. After your attorney has petitioned the court, creditors are required to stop contacting you. Foreclosure and other actions cease, and there’s a calm period that allows you to regroup. Most people do not expect their lives to suddenly experience lower stress and anxiety.
The process may entail a meeting with creditors, although many often opt not to attend. A bankruptcy trustee will likely be assigned to your case to oversee asset liquidation or debt repayment to some degree. In Chapter 7 cases, you can start rebuilding your credit. In Chapter 13 cases, the 3- to 5-year repayment plan lowers monthly obligation so that you can enjoy an improved quality of life.
How to Work with an Experienced, Cost-effective Virginia Bankruptcy Attorney
As the saying goes, “the devil is in the details,” and you and your bankruptcy lawyer will negotiate a fairly rigorous court process. One of the pertinent reasons to work with an attorney who handles bankruptcy cases on a regular basis is because legal missteps can be costly. These are the steps you and your legal representative generally must negotiate.
- Schedule a Bankruptcy Consultation: At the initial meeting with your lawyer, debts and assets will be reviewed to determine whether you qualify for bankruptcy. You will need to bring pertinent financial documents that your attorney will request prior to the consultation.
- Chapter 7 or 13 Eligibility: Your attorney will likely walk you through the Chapter 7 means test and decide if this is a viable option. If not, the secured and unsecured debt ceiling for Chapter 13 may be considered.
- Attend Credit Counseling: Bankruptcy filers are required to complete credit counseling within the 180 days before they file. This can be completed online or over the phone and takes approximately 30-45 minutes. The Agarwal Law Firm includes this charge as part of the fees you pay to the law firm; ask your bankruptcy attorney if credit counselling is included in your overall costs.
- Documentation: Gather all necessary financial records to support the filing. Creditors may also review these items.
- Creditors Meeting: The bankruptcy trustee assigned to your case will likely schedule a creditors meeting. You may be required to attend to discuss repayment options.
- Financial Management Requirement: To receive a bankruptcy discharge, filers are generally required to complete a course on financial management.
- Receive Your Discharge: Those who file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy and complete all the requirements may receive a full discharge within 2-3 months. Chapter 13 bankruptcy is subject to the terms of the approved repayment plan.
Although the bankruptcy process requires legal precision, knowledge, and experience to navigate, it remains far less stressful than trying to climb out of debt without the necessary financial resources. Everyday Americans have a right to live the best possible life, which is why bankruptcy is a critical legal tool.
Life After Bankruptcy
The process of restoring financial normalcy begins immediately after filing for bankruptcy. If you select Chapter 7, debts may be promptly discharged and you can start rebuilding your credit. Although the bankruptcy remains on your credit history for up to 10 years, it usually takes about two years to rebuild and there are credit resources available to those who have successfully discharged debt.
If you work diligently to re-establish a strong credit history, home loans can be available within only a few years. The reality of life after bankruptcy is that following the lengthy recession, lenders and financial institutions came to grips with the fact that many Americans have had to use bankruptcy protection. Bankruptcy filers are now fully able to move forward with modest limitations. And, those who navigate the more complex Chapter 13 process are able to keep vital assets and maintain resources.
In many ways, life after bankruptcy may be preferable to suffering insurmountable debt. The first step toward securing a more robust, debt-free future is by contacting an experienced Virginia law firm and scheduling a consultation.
Virginia Bankruptcy Help: The Agarwal Law Firm
At The Agarwal Law Firm, our goal is to ensure that every American considering bankruptcy understands their options and has the guidance to make the right decision for their financial future. We provide Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy services in Richmond, Virginia. If you have any questions about your options and what type of bankruptcy you qualify for, don’t hesitate to contact us. One of our Virginia bankruptcy attorneys will get in touch to help.